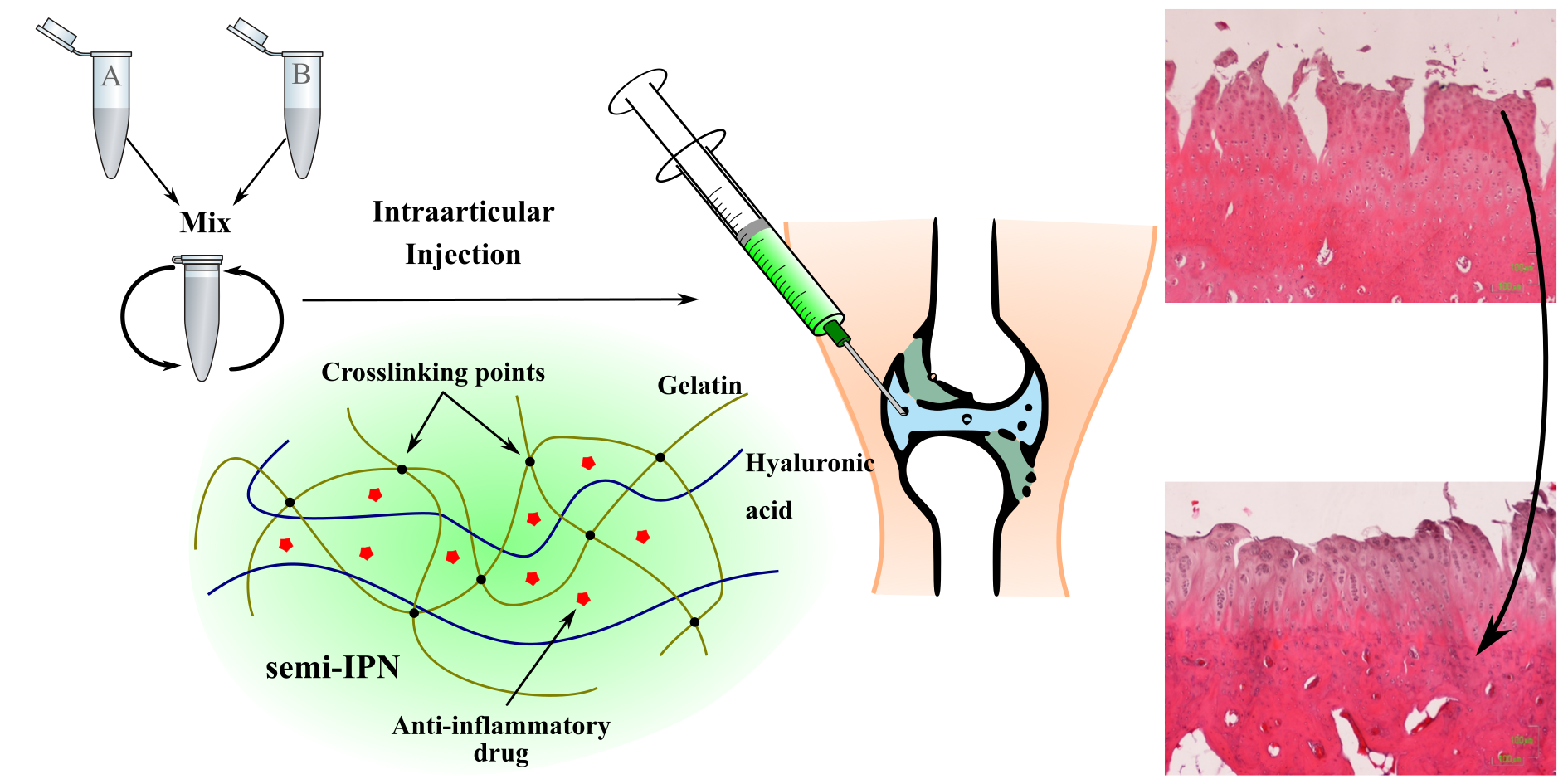
Osteoarthrosis is a chronic degenerative disease of slow progression that constitutes a severe clinical and public health problem. The current clinical treatments available are incapable to reverse disease progression so that nowadays there is a demand of developing alternative systems to avoid or delay the application of surgical procedures. In this work, injectable hydrogel drug delivery systems loaded with naproxen or dexamethasone are formulated based on a ready to use simple two components system. Hydrogels consist of gelatin and hyaluronic acid forming a semi-interpenetrating network structure (semi-IPN). This study mainly focuses on the physicochemical characterization of hydrogels, the in vitro analysis and in vivo performance after injection in New Zealand rabbit knees with an OA model. Results indicate that there is a close relationship between the drug release and the hydrogel degradation. All hydrogels are cytocompatible and support good cell viability of human chondrocytes and osteoblast. The in vivo results reveal that both hydrogels promote cartilage regeneration after their injection in osteoarthrosis knees. The extracellular matrix reflects presence of proteoglycans for the naproxen loaded hydrogel group, and collagen type II expression in both loaded groups, more evident for that containing dexamethasone.
3729048
{3729048:6N8HWE2Z}
nature
50
1
1
title
661
http://www.biomateriales.ictp.csic.es/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3A%22zotpress-9469968bd613a6858575e3fcc528b09a%22%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%226N8HWE2Z%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A3729048%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-Fern%5Cu00e1ndez%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222020-05-01%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A2%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3EGarc%5Cu00eda-Fern%5Cu00e1ndez%2C%20L.%20%3Ci%3Eet%20al.%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ca%20target%3D%27_blank%27%20href%3D%27http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0928493119340500%27%3EInjectable%20hydrogel-based%20drug%20delivery%20system%20for%20cartilage%20regeneration%3C%5C%2Fa%3E.%20%3Ci%3EMaterials%20Science%20and%20Engineering%3A%20C%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Cb%3E110%3C%5C%2Fb%3E%2C%20110702%20%282020%29.%20%3Ca%20title%3D%27Cite%20in%20RIS%20Format%27%20class%3D%27zp-CiteRIS%27%20href%3D%27http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomateriales.ictp.csic.es%5C%2Fwp-content%5C%2Fplugins%5C%2Fzotpress%5C%2Flib%5C%2Frequest%5C%2Frequest.cite.php%3Fapi_user_id%3D3729048%26amp%3Bitem_key%3D6N8HWE2Z%27%3ECite%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22Injectable%20hydrogel-based%20drug%20delivery%20system%20for%20cartilage%20regeneration%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Luis%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-Fern%5Cu00e1ndez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Marta%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Olmeda-Lozano%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lorena%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Benito-Garz%5Cu00f3n%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Antonio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22P%5Cu00e9rez-Caballer%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Julio%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22San%20Rom%5Cu00e1n%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Blanca%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22V%5Cu00e1zquez-Lasa%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22%22%2C%22date%22%3A%22May%201%2C%202020%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.1016%5C%2Fj.msec.2020.110702%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%220928-4931%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.sciencedirect.com%5C%2Fscience%5C%2Farticle%5C%2Fpii%5C%2FS0928493119340500%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%22HBGS28EX%22%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222020-02-12T10%3A41%3A56Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D