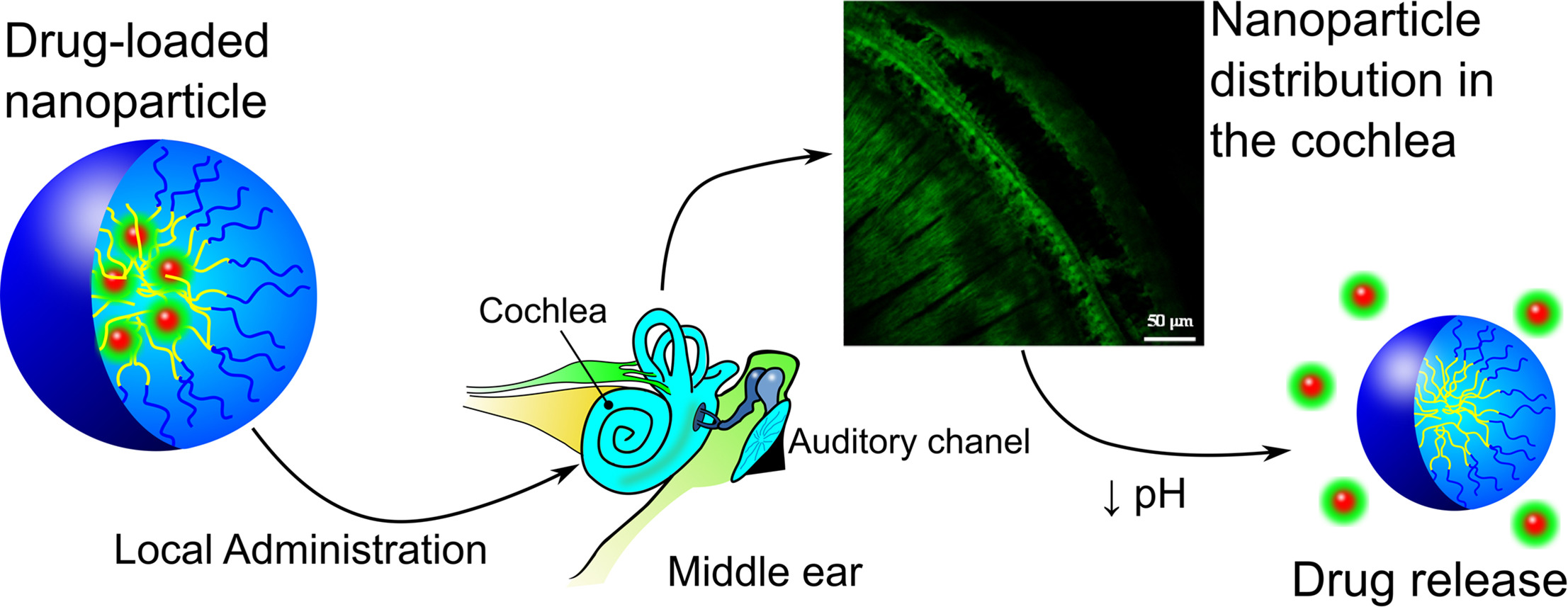
Polymeric nanoparticles (NP) based on smart synthetic amphiphilic copolymers are used to transport and controlled release dexamethasone in the inner ear to protect against the ototoxic effect of cisplatin. The NP were based on a mixture of two pseudo-block polymer drugs obtained by free radical polymerization: poly(VI-co-HEI) and poly(VP-co-MVE) or poly(VP-co-MTOS), being VI 1-vinylimidazole, VP N-vinylpyrrolidone, and IBU, MVE and MTOS the methacrylic derivatives of ibuprofen, α-tocopherol and α-tocopheryl succinate, respectively. The NP were obtained by nanoprecipitation with appropriate hydrodynamic properties, and isoelectric points that matched the pH of inflamed tissue. The NP were tested both in vitro (using HEI-OC1 cells) and in vivo (using a murine model) with good results. Although the concentration of dexamethasone administered in the nanoparticles is around two orders of magnitude lower that the conventional treatment for intratympanic administration, the NP protected from the cytotoxic effect of cisplatin when the combination of the appropriate properties in terms of size, zeta potential, encapsulation efficiency and isoelectric point were achieved. To the best of our knowledge this is the first time that pH sensitive NP are used to protect from cisplatin-induced hearing loss by intratympanic administration.