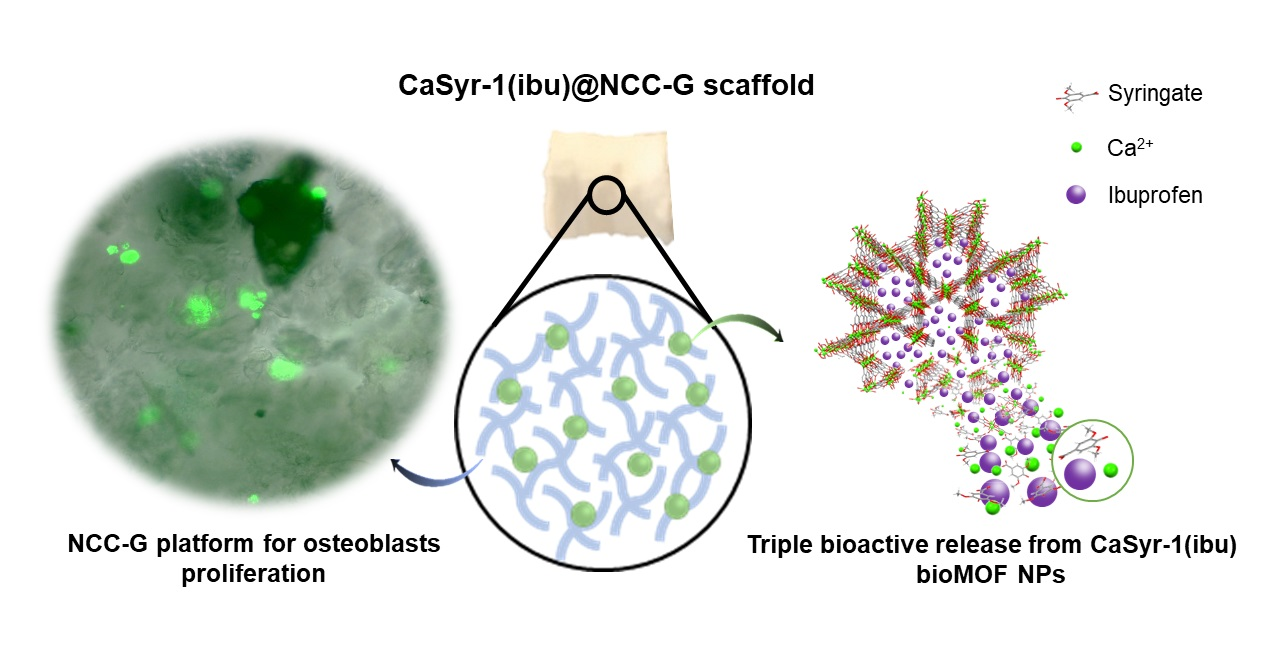
The development of new biomaterials for musculoskeletal tissue repair is currently an important branch in biomedicine research. The approach presented here is centered around the development of a prototypic synthetic glycerogel scaffold for bone regeneration, which simultaneously features therapeutic activity. The main novelty of this work lies in the combination of an open meso and macroporous nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC)-based glycerogel with a fully biocompatible microporous bioMOF system (CaSyr-1) composed of calcium ions and syringic acid. The bioMOF framework is further impregnated with a third bioactive component, i.e., ibuprofen (ibu), to generate a multifold bioactive system. The integrated CaSyr-1(ibu) serves as a reservoir for bioactive compounds delivery, while the NCC scaffold is the proposed matrix for cell ingrowth, proliferation and differentiation. The measured drug delivery profiles, studied in a phosphate-buffered saline solution at 310 K, indicate that the bioactive components are released concurrently with bioMOF dissolution after ca. 30 min following a pseudo-first-order kinetic model. Furthermore, according to the semi-empirical Korsmeyer-Peppas kinetic model, this release is governed by a case-II mechanism, suggesting that the molecular transport is influenced by the relaxation of the NCC matrix. Preliminary in vitro results denote that the initial high concentration of glycerol in the NCC scaffold can be toxic in direct contact with human osteoblasts (HObs). However, when the excess of glycerol is diluted in the system (after the second day of the experiment), the direct and indirect assays confirm full biocompatibility and suitability for HOb proliferation.
3729048
{3729048:TJPZ2YW8}
1
nature
50
default
1
1
title
1712
http://www.biomateriales.ictp.csic.es/wp-content/plugins/zotpress/
%7B%22status%22%3A%22success%22%2C%22updateneeded%22%3Afalse%2C%22instance%22%3Afalse%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22request_last%22%3A0%2C%22request_next%22%3A0%2C%22used_cache%22%3Atrue%7D%2C%22data%22%3A%5B%7B%22key%22%3A%22TJPZ2YW8%22%2C%22library%22%3A%7B%22id%22%3A3729048%7D%2C%22meta%22%3A%7B%22creatorSummary%22%3A%22Rosado%20et%20al.%22%2C%22parsedDate%22%3A%222024-10%22%2C%22numChildren%22%3A1%7D%2C%22bib%22%3A%22%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-bib-body%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22line-height%3A%202%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-entry%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22clear%3A%20left%3B%20%5C%22%3E%5Cn%20%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-left-margin%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22float%3A%20left%3B%20padding-right%3A%200.5em%3B%20text-align%3A%20right%3B%20width%3A%201em%3B%5C%22%3E1.%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%3Cdiv%20class%3D%5C%22csl-right-inline%5C%22%20style%3D%5C%22margin%3A%200%20.4em%200%201.5em%3B%5C%22%3ERosado%2C%20A.%20%3Ci%3Eet%20al.%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Ca%20class%3D%27zp-ItemURL%27%20target%3D%27_blank%27%20href%3D%27https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F2310-2861%5C%2F10%5C%2F10%5C%2F631%27%3EBioMOF%40cellulose%20Glycerogel%20Scaffold%20with%20Multifold%20Bioactivity%3A%20Perspective%20in%20Bone%20Tissue%20Repair%3C%5C%2Fa%3E.%20%3Ci%3EGels%3C%5C%2Fi%3E%20%3Cb%3E10%3C%5C%2Fb%3E%2C%20631%20%282024%29.%20%3Ca%20title%3D%27Cite%20in%20RIS%20Format%27%20class%3D%27zp-CiteRIS%27%20href%3D%27http%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.biomateriales.ictp.csic.es%5C%2Fwp-content%5C%2Fplugins%5C%2Fzotpress%5C%2Flib%5C%2Frequest%5C%2Frequest.cite.php%3Fapi_user_id%3D3729048%26amp%3Bitem_key%3DTJPZ2YW8%27%3ECite%3C%5C%2Fa%3E%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%20%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%5Cn%3C%5C%2Fdiv%3E%22%2C%22data%22%3A%7B%22itemType%22%3A%22journalArticle%22%2C%22title%22%3A%22BioMOF%40cellulose%20Glycerogel%20Scaffold%20with%20Multifold%20Bioactivity%3A%20Perspective%20in%20Bone%20Tissue%20Repair%22%2C%22creators%22%3A%5B%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Albert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rosado%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Alejandro%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Borr%5Cu00e1s%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Miguel%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22S%5Cu00e1nchez-Soto%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Magdal%5Cu00e9na%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Lab%5Cu00edkov%5Cu00e1%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Hubert%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Hettegger%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Rosa%20Ana%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ram%5Cu00edrez-Jim%5Cu00e9nez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lu%5Cu00eds%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Rojo%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Lu%5Cu00eds%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Garc%5Cu00eda-Fern%5Cu00e1ndez%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Mar%5Cu00eda%20Rosa%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Aguilar%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Falk%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Liebner%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Ana%20M.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22L%5Cu00f3pez-Periago%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Jos%5Cu00e9%20A.%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Ayll%5Cu00f3n%22%7D%2C%7B%22creatorType%22%3A%22author%22%2C%22firstName%22%3A%22Concepci%5Cu00f3n%22%2C%22lastName%22%3A%22Domingo%22%7D%5D%2C%22abstractNote%22%3A%22The%20development%20of%20new%20biomaterials%20for%20musculoskeletal%20tissue%20repair%20is%20currently%20an%20important%20branch%20in%20biomedicine%20research.%20The%20approach%20presented%20here%20is%20centered%20around%20the%20development%20of%20a%20prototypic%20synthetic%20glycerogel%20scaffold%20for%20bone%20regeneration%2C%20which%20simultaneously%20features%20therapeutic%20activity.%20The%20main%20novelty%20of%20this%20work%20lies%20in%20the%20combination%20of%20an%20open%20meso%20and%20macroporous%20nanocrystalline%20cellulose%20%28NCC%29-based%20glycerogel%20with%20a%20fully%20biocompatible%20microporous%20bioMOF%20system%20%28CaSyr-1%29%20composed%20of%20calcium%20ions%20and%20syringic%20acid.%20The%20bioMOF%20framework%20is%20further%20impregnated%20with%20a%20third%20bioactive%20component%2C%20i.e.%2C%20ibuprofen%20%28ibu%29%2C%20to%20generate%20a%20multifold%20bioactive%20system.%20The%20integrated%20CaSyr-1%28ibu%29%20serves%20as%20a%20reservoir%20for%20bioactive%20compounds%20delivery%2C%20while%20the%20NCC%20scaffold%20is%20the%20proposed%20matrix%20for%20cell%20ingrowth%2C%20proliferation%20and%20differentiation.%20The%20measured%20drug%20delivery%20profiles%2C%20studied%20in%20a%20phosphate-buffered%20saline%20solution%20at%20310%20K%2C%20indicate%20that%20the%20bioactive%20components%20are%20released%20concurrently%20with%20bioMOF%20dissolution%20after%20ca.%2030%20min%20following%20a%20pseudo-first-order%20kinetic%20model.%20Furthermore%2C%20according%20to%20the%20semi-empirical%20Korsmeyer-Peppas%20kinetic%20model%2C%20this%20release%20is%20governed%20by%20a%20case-II%20mechanism%2C%20suggesting%20that%20the%20molecular%20transport%20is%20influenced%20by%20the%20relaxation%20of%20the%20NCC%20matrix.%20Preliminary%20in%20vitro%20results%20denote%20that%20the%20initial%20high%20concentration%20of%20glycerol%20in%20the%20NCC%20scaffold%20can%20be%20toxic%20in%20direct%20contact%20with%20human%20osteoblasts%20%28HObs%29.%20However%2C%20when%20the%20excess%20of%20glycerol%20is%20diluted%20in%20the%20system%20%28after%20the%20second%20day%20of%20the%20experiment%29%2C%20the%20direct%20and%20indirect%20assays%20confirm%20full%20biocompatibility%20and%20suitability%20for%20HOb%20proliferation.%22%2C%22date%22%3A%222024%5C%2F10%22%2C%22language%22%3A%22en%22%2C%22DOI%22%3A%2210.3390%5C%2Fgels10100631%22%2C%22ISSN%22%3A%222310-2861%22%2C%22url%22%3A%22https%3A%5C%2F%5C%2Fwww.mdpi.com%5C%2F2310-2861%5C%2F10%5C%2F10%5C%2F631%22%2C%22collections%22%3A%5B%5D%2C%22dateModified%22%3A%222024-10-03T09%3A17%3A57Z%22%7D%7D%5D%7D